Giacomo Lanzi
Giacomo Lanzi
Zombie phishing: beware of emails, it could be zombies
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Out of nowhere, someone replies to an email conversation dated months ago. This is a real conversation that actually happened. Maybe it’s about a meeting, a job opportunity. This email seems very relevant, but beware, it could be zombie phishing .
Indeed, something is wrong, the topic discussed has been over for months and now there is a strange error message in the body of the email. This is a sneaky tactic: revive a long dead email conversation.

Not the usual phishing
The Cofense ™ Phishing Defense Center ™ (PDC) spotted a large Zombie Phishing campaign in 2018. The scam , like almost any phishing attack, is carried out through compromised email accounts.
Scammers take over an email account and respond to long-closed conversations with a phishing link or malicious attachment (e.g. malware or a keylogger ) . Since the email subject is usually relevant to the victim, a curiosity-driven click is very likely to occur . In fact, let’s not forget that the original conversation was already present in the messages received, it is easy to think that it is a follow up or similar.
These Zombie Phishing attacks appear to use automatically generated infection URLs to evade detection. No two links are alike, and they are hidden behind “error” messages without too many frills in the body of the message. This scenario provides a pattern of apparent legitimacy for the users who are victims.
The zombies in computer science
In the computer industry, a zombie is a compromised computer connected to the network. The compromised state could be due to a hacker, virus, malware, or trojan horse .
The infected machine performs malicious tasks under a remote direction. Zombie computer botnets are often used to spread email spam and launch denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
Types of attack
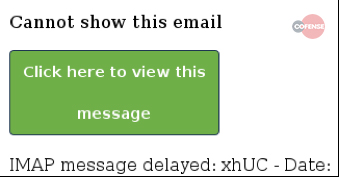
Here are some observed patterns of Zombie Phishing carrying malicious links . A distinguishing factor was the use of two distinct graphic templates containing button or link error messages.
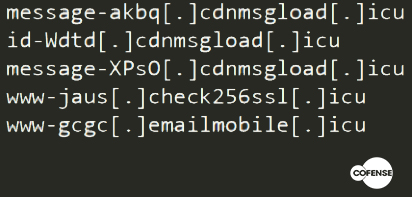
The message reads something like “Incomplete message” or “Inability to show the whole message”. The link or button invites you to click to see the original message. Obviously the click only involves the installation of a malware or other similar events . Note that no two identical links have been identified, a sign that probably a bot was generating the addresses.
Another common factor is the use of domains with the .icu TLD. This is probably a factor that varies considerably over time. Here are some of the domains found in the first analysis of 2018:
These zombie phish attacks have been observed to use official organizational logos to add legitimacy to the fake login pages. A common practice in phishing techniques that we have already seen in other articles.
Landing pages are designed to look like a legitimate online portal, including a company logo and even a favicon. In these cases the ultimate goal is the theft of the victim’s credentials .
Furthermore, any victim who visits the malicious website is “tagged” using the host’s IP address as an identifier and, after entering the credentials, is directed to the same spam website seen by other victims. This is often done via obfuscated links using URL shorteners (such as hxxps://href[.]Li/).
If the same host tries to visit the phishing link again, the fake login page is skipped and you are forwarded directly to the spam page. This markup and URL shortener obfuscation helps attackers keep a low profile and continue their campaign unabated.
Conversation Hijacking

The conversation hijacking tactic is by no means new and is now living a new life with zombie phishing . Scammers have hijacked compromised email accounts to distribute malware and phishing emails as replies to conversations that have been concluded for years now.
This technique is still popular because it makes victims much more likely to click on links and download or open files. The threshold of attention against classic phishing attacks is lowered when messages are brought into conversations already in their inbox .
A couple of years old example of this was the botnet Geodo . Basically it is insertion into existing email threads ( conversation hijacking ) to deliver malicious documents. These, in turn, download a sample of Geodo or other malware such as Ursnif , which according to Key4Biz was the most widespread in Italy in June 2020.
However, the effectiveness of this tactic can greatly depend on the content of the conversations . A reply to an automated advertising email is less likely to cause an infection than a reply to a help-desk support thread.
There have been several Geodo zombie phishing campaigns consisting of replies to automated advertising emails. This is an indication that, in some cases, campaigns consist of indiscriminate replies to all emails in a mailbox. Since the volume of these conversation hijacking is still relatively low, the small reach of these emails is probably limited by the number of ongoing conversations .
Certain account types are therefore more likely to attract the direct attention of threat actors and induce them to invest additional effort and time in developing unique phishing campaigns for those accounts.
Defense from zombie-phishing
Here are some quick tips to avoid losing your credentials in a Zombie Phishing attack:
- Beware of email subjects that may seem relevant but come from old conversations
- Beware of any error message in the body of the message
- Don’t trust attached documents just because they’re replying to a conversation
- Hover your mouse over buttons or links in suspicious messages to check for suspicious domains
It has been observed that these campaigns have gotten smarter . To combat this and other forms of phishing, employee training is key.
A properly trained workforce is what it takes to defend your organization against Zombie Phishing attacks.
SOD offers a full service in this regard . We begin by attacking the company in a controlled manner, testing any weaknesses in employee safety or behavior. Subsequently, specific training is designed to remedy the gaps and fully train the staff.
To keep defenses high, our SOCaaS includes the analysis of user behavior, logs of connected machines and the network in a to immediately identify phishing attempts.
Useful links:
Customers
Twitter FEED
Recent activity
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes L'impatto crescente delle minacce informatiche, su sistemi operativi privati op… https://t.co/FimxTS4o9G
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The growing impact of cyber threats, on private or corporate operating systems… https://t.co/y6G6RYA9n1
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Tempo di lettura stimato: 6 minuti Today we are talking about the CTI update of our services. Data security is… https://t.co/YAZkn7iFqa
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes Il tema della sicurezza delle informazioni è di grande attualità in questo peri… https://t.co/tfve5Kzr09
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The issue of information security is very topical in this historical period ch… https://t.co/TP8gvdRcrF
Newsletter
{subscription_form_1}© 2024 Cyberfero s.r.l. All Rights Reserved. Sede Legale: via Statuto 3 - 42121 Reggio Emilia (RE) – PEC [email protected] Cod. fiscale e P.IVA 03058120357 – R.E.A. 356650 Informativa Privacy - Certificazioni ISO