Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
I dati di threat intelligence forniscono alle aziende approfondimenti rilevanti e tempestivi necessari per comprendere, prevedere, rilevare e rispondere alle minacce alla sicurezza informatica. Le soluzioni di intelligence sulle minacce raccolgono, filtrano e analizzano grandi volumi di dati grezzi relativi a fonti esistenti o emergenti di minacce. Il risultato sono feed di threat intelligence e rapporti di gestione. I data scientist e i team di sicurezza utilizzano questi feed e report per sviluppare un programma con risposte mirate agli incidenti per attacchi specifici.
Tutti, dalla prevenzione delle frodi alle operazioni di sicurezza all’analisi dei rischi, traggono vantaggio dalla threat intelligence. Il software di intelligence sulle minacce fornisce visualizzazioni interattive e in tempo reale dei dati relativi alle minacce e alle vulnerabilità.
Il vantaggio offerto agli analisti ed esperti di sicurezza è evidente e serve a identificare facilmente e rapidamente i modelli degli attori delle minacce. Comprendere la fonte e l’obiettivo degli attacchi aiuta i capi d’azienda a mettere in atto difese efficaci per mitigare i rischi e proteggersi dalle attività che potrebbero avere un impatto negativo sull’azienda.
La cyber threat intelligence può essere classificata come strategica, tattica oppure operativa. Quella Strategica riguarda le capacità e gli intenti generali degli attacchi informatici. Di conseguenza anche lo sviluppo di strategie informate associate alla lotta contro le minacce a lungo termine. Quella Tattica riguarda le tecniche e le procedure che gli aggressori potrebbero utilizzare nelle operazioni quotidiane. Infine, la threat intelligence Operativa, fornisce informazioni altamente tecniche a livello forense riguardanti una specifica campagna di attacco.

Il ciclo della threat intelligence
Le soluzioni di intelligence sulle minacce raccolgono dati grezzi sugli attori e le minacce da varie fonti. Questi dati vengono poi analizzati e filtrati per produrre feed e rapporti di gestione che contengono informazioni che possono essere utilizzate in soluzioni automatizzate di controllo della sicurezza. Lo scopo principale di questo tipo di sicurezza è quello di mantenere le organizzazioni informate sui rischi delle minacce persistenti avanzate, delle minacce zero-day e degli exploit, e su come proteggersi da esse.
Il ciclo di intelligence delle minacce informatiche consiste nelle seguenti fasi.
Pianificazione: I requisiti dei dati devono essere prima definiti.
Raccolta: Si raccolgono grandi quantità di dati grezzi da fonti interne ed esterne di threat intelligence.
Elaborazione: I dati grezzi sono filtrati, categorizzati e organizzati.
Analisi: Questo processo trasforma i dati grezzi in flussi di informazioni sulle minacce con l’uso di tecniche analitiche strutturate in tempo reale e aiuta gli analisti a individuare gli indicatori di compromissione (IOC).
Diffusione: I risultati dell’analisi vengono immediatamente condivisi con i professionisti della sicurezza informatica e gli analisti di threat intelligence.
Feedback: Se tutte le domande trovano risposta, il ciclo si conclude. Se ci sono nuovi requisiti, il ciclo ricomincia dalla fase di pianificazione.
Indicatori comuni di compromissione
Le aziende sono sempre più sotto pressione per gestire le vulnerabilità della sicurezza e il panorama delle minacce è in continua evoluzione. I feed di threat intelligence possono aiutare in questo processo identificando gli indicatori comuni di compromissione (IOC). Non solo, possono anche raccomandare i passi necessari per prevenire attacchi e infezioni. Alcuni degli indicatori di compromissione più comuni includono:
Indirizzi IP, URL e nomi di dominio: Un esempio potrebbe essere un malware che prende di mira un host interno che sta comunicando con un noto attore di minacce.
Indirizzi e-mail, oggetto delle e-mail, link e allegati: Un esempio potrebbe essere un tentativo di phishing che si basa su un utente ignaro che clicca su un link o un allegato e avvia un comando dannoso.
Chiavi di registro, nomi di file e hash di file e DLL: Un esempio potrebbe essere un attacco da un host esterno che è già stato segnalato per un comportamento nefasto o che è già infetto.

Quali strumenti per la threat intelligence
Il crescente aumento del malware e delle minacce informatiche ha portato a un’abbondanza di strumenti di threat intelligence che forniscono preziose informazioni per proteggere le aziende.
Questi strumenti si presentano sotto forma di piattaforme sia open source che proprietarie. Queste forniscono una serie di capacità di difesa contro le minacce informatiche, come l’analisi automatizzata dei rischi, la raccolta di dati privati, strumenti di ricerca rapida di threat intelligence, la segnalazione e condivisione di queste informazioni tra più utenti, avvisi curati, analisi dei rischi di vulnerabilità, monitoraggio del dark web, mitigazione automatizzata dei rischi, threat hunting e molto altro.
Abbiamo parlato di uno di questi strumenti in un altro articolo: il Mitre Att&ck. Questo è uno strumento molto utile per conoscere i comportamenti e le tecniche di attacco hacker. Questo grazie alle informazioni raccolte dalla threat intelligence e la conseguente condivisione. Un framework come questo è molto efficiente per creare meccanismi difensivi che consentono di mettere in sicurezza le infrastrutture aziendali.
Intelligenza artificiale e informazioni sulle minacce
Come abbiamo visto prima, la raccolta di informazioni da varie fonti non è altro che una delle fasi. Queste devono poi venire analizzate e successivamente elaborate in protocolli di controllo, per essere davvero utili per la sicurezza.
Per questo tipo di lavori di analisi, definizione di comportamenti baseline e controllo dei dati ci si affida sempre di più all’intelligenza artificiale e al deep learning. Un Next Generation SIEM, affiancato a una soluzione UEBA sono perfetti per questo tipo di protezione.
Il controllo del comportamento delle entità all’interno del perimetro effettuato dal UEBA è in grado di identificare ogni comportamento sospetto, in base alle informazioni raccolte e analizzate dal SIEM.
Conclusioni
Gli strumenti di difesa che abbiamo nominato sono il valore primario di un piano di sicurezza aziendale. Adottare soluzioni specifiche, implementare la threat intelligence e quindi una ricerca attiva degli indicatori di minacce, offre una posizione di vantaggio strategica. L’azienda può operare un passo avanti ai criminali, i quali possono far leva solo sull’effetto sorpresa contro le loro vittime. Proprio per questa situazione generale, ogni azienda dovrebbe essere nelle condizioni di non farsi cogliere alla sprovvista. Implementare soluzioni proattive è ormai necessario.
La threat intelligence è quindi un’arma da difesa dietro la quale mettere al riparo le risorse più importanti per poter lavorare in tranquillità.
Se vuoi sapere come possiamo aiutarti con i nostri servizi dedicati alla sicurezza, non esitare a contattarci, saremo lieti di rispondere a ogni domanda.
Useful links:
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) – maggiore efficacia per la sicurezza IT
Progetti di Secure Online Desktop
Cos’è la Cyber Security? Definizione e proposte
Prevenire il shoulder surfing e il furto di credenziali aziendali

Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
The issue of information security is very topical in this historical period characterized by digitization. To protect themselves, businesses and individuals can use a variety of tools that can prevent an attack, but also help manage it. In this article we talk about Automated Response Integration and the automations in the SOCaaS offered by SOD .
Although the systems used are almost always based on efficient technologies, in recent years the implementation of SOCaaS services equipped with SNYPR for the analysis of Big Data is making a difference. The dedicated SOCaaS services facilitate end users in the use of security systems, basing their operation on automatic processes that protect company devices.

What is Automated Response Integration
The term Automated Response Integration identifies a specific approach to data analysis and consequent response in a cyber defense scenario. We see it today, in particular, related to our SOCaaS on which the SNYPR tool is applied, which we have already talked about in the past.
SNYPR and Automated Response Integration
In order to understand the potential of a SOCaaS service, with the implementation of SNYPR, it is appropriate to understand first what is meant by this term. When the word SNYPR is used, it identifies that examination tool capable of analyzing Big Data and simplifying its actions . A system equipped with SNYPR can examine a huge amount of data and identify the behaviors of everyone who interacts with the platform.
There is the combination of SIEM and UEBA logs, as well as an analysis dedicated to security in real time, very useful for automating the daily operations carried out in the infrastructure.
The operation of a SNYPR tool for corporate IT is based on the analysis of thousands of information collected, thanks to artificial intelligence. These analyzes are then used to prevent and intervene on cyber threats. The fact that most of these operations are automatic brings us to the field of Automated Response Integration.
Technically it differs from other platforms in the use of threat detection algorithms that have the ability to scan systems and logins performed by other devices in real time . A traditional system simply collects data, while a SOCaaS with SNYPR implementation can also detect much more harmful threats and adapt accordingly.
The strengths of Automated Response Integration with SNYPR / SOCaaS
One of the strengths of this tool is its Security Data Lake (SDL) based security system. This condition allows companies to keep a copy of the data in the SDL and submit the scan request at any time. There is no data lock, as in traditional systems, but an open system capable of sharing information with the different devices.
As it is easy to guess, it is precisely this availability of data and the possibility of in-depth analysis, which allows us to implement an Automated Response Integration strategy with our SOCaaS.
There are various system functions in the field that are noteworthy. These include: data enrichment, distributed behavioral analysis, historical investigation, scalability and data redundancy.
This coordination of services allows to have a concrete impact for IT security , a condition evident in three areas of SNYPR competence: internal threats, persistent threats and professional use.
The professional use of SNYPR: in recent years, the most important companies have equipped themselves with a SNYPR platform to protect their data storage and analysis infrastructures. The system constantly monitors the flow of information and adapts to the best conditions in the event of cyber attacks.
Automated Response Integration for automation in SOCaaS
From a technical point of view, a SNYPR system itself guarantees excellent potential, but it is with the SOCaaS implementation that it finds its maximum protection expression in IT systems.
The analysis of threats in a company system, although it is carried out in real time, requires the intervention of specialized technicians to identify the problem. With SOCaaS, identification is linked to automated actions to deal with possible threats, without the need for third-party intervention.
There is a real integration with automated response useful to prevent and eradicate possible threats . This process is essential not only to prevent business systems from being compromised, but also to protect companies and their IT departments, which can focus on other tasks.
Automated Response Integration functionality
Playbook: the tool can launch a playbook when SNYPR threats are detected. The transcript of the events is important to understand the origin of the threat.
Query: automation can manage actions or queries on end points directly from SNYPR, in order to face the cyber attack. This feature avoids the blocking of production in the most excited moments.
UEBA: As mentioned in the previous lines, an NSYPR-based tool can import UEBA alerts. The reference formats are usually CEF, which report warnings from any type of device, significantly affecting safety.
IP control : one of the strengths of this technology is the control of domains, IPs, files and URLs, ensuring maximum versatility for any type of work activity.
DNS and Whols data : The automated response is particularly useful in storing DNS and Whols data, as it is possible to check the validity of certificates and monitor unwanted access.
Vulnerability: You can schedule a network vulnerability scan. This analysis process is especially suitable for companies that send and receive a large flow of information outside the company context.

Relying on professionals
Not all SOCaaS-based services that implement SNYPR are identical to each other, some of them offer the same technology but different intervention methods. Among the most interesting solutions is our SOCaaS. For years we have been dealing with offering IT security solutions internationally and this is a guarantee of excellence, alongside our certifications and partnerships.
Our IT security service, based on Automated Response Integration, guarantees complete monitoring of corporate infrastructures, helping the company to avoid additional costs for ordinary or extraordinary maintenance of the devices.
Conclusions
The implementation of SOCaaS automated systems is now essential for companies that want to protect themselves from IT docking. Real-time analysis and notification of potential threats ensure essential peace of mind in an age increasingly exposed to digital dangers.
To find out how SOD and its services can help your company, do not hesitate to contact us, we will be happy to answer any questions.
Useful links:

Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
When we refer to artificial intelligence, we often refer to the great technologies that could control the world, with an obvious streak of science fiction. The reality is very different and is characterized by a technology with great potential, which is able to ensure countless advantages . Today we talk about how artificial intelligence can be implemented in monitoring.
The use of these technologies is unavoidably transversal to many sectors of the economy, but it is also usable in some aspects of everyday life. Some examples range from washing machines that, weighing the load of laundry, are able to choose the most advantageous washing program, to voice assistants that simplify our everyday life.
Very important in the corporate sector are the monitoring systems which were created precisely from these technologies which we will talk more about in a moment.
Thanks to the optimization of the computing capacity operated by artificial intelligence, it is possible to increase the efficiency of company equipment. Let’s see how.

What is artificial intelligence and how can it innovate monitoring ?
Today, artificial intelligence is declined in many ways. Perhaps the most important is processing a large amount of data then providing answers to complex questions. At the base of artificial intelligence there is the study of algorithms that deal with performing complex mathematical operations.
Artificial intelligence is a very useful tool within a company, as it is able to carry out very sophisticated and precise processing. These operations are capable of significantly improving the operations and productivity of numerous departments of the company itself.
Applied to monitoring, for example, artificial intelligence is capable of analyzing the logs coming from the network, both in terms of performance and behavior. The big step forward in the analysis and monitoring of an infrastructure consists precisely in recognizing whether certain behaviors that emerge from the logs are risky or not.
To achieve these results it is essential to have all those features that are available through artificial intelligence .
What are the advantages of using artificial intelligence for monitoring?
Artificial intelligence is able to provide companies that choose to use it countless advantages. Not only in terms of improving the performance of information systems, but also to make more efficient and improve the security of the same, preventing attacks.
This happens thanks to the analysis of the logs both from a technical and a behavioral point of view. Technical analysis highlights any ongoing problems, while behavioral analysis can prevent or immediately identify suspicious actions.
How can our monitoring system improve business efficiency?
Our monitoring system is able to improve business efficiency through numerous technical analyzes in able to be implemented not only on the entire system, but also on individual units.
The ability to analyze data in depth also allows you to improve the management of the entire IT structure and prevent overloads or attacks. Overall, the efficiency and safety of the infrastructure are increased at the same time through artificial intelligence applied to monitoring.
But there’s more: these analysis and monitoring systems are able to integrate with extreme effectiveness in complex architectures. By being able to analyze large amounts of data and being able to deduce behaviors and actions from these, efficiency in security is ensured.
Another advantage is the fact that this monitoring system does not require specific hardware. Software agents are installed on the systems to be controlled which have the sole task of sending data in the form of a log to the control system. analyses.
These systems therefore prove to be the ideal solution to keep large and small IT architectures under control, with the aim of improving efficiency and increasing overall security. In short, an application really interesting and useful of artificial intelligence in monitoring.

What are the fields of application of this technology?
We apply artificial intelligence systems to monitoring, benefiting our customers enormously. First we can collect large amounts of data, enrich it automatically and finally analyze it. The analyzes are carried out both from a technical and a behavioral point of view.
The result is a dedicated system, our SOCaaS, which makes risk mitigation extremely efficient, particularly quick intervention in the event of an anomaly and also provides regular reports.
This service is able to bring together all the features listed in the article, and to offer it as a solution for companies that want a superior security system.
Better efficiency, safety, versatility, operability, are just some of the paradigms used to define the services we make available to our customers. Our main goal is to simplify and make your company’s IT security more efficient.
Do not hesitate to contact us if you want to know more, we will be happy to answer any questions.
Useful links:

Estimated reading time: 7 minutes
When we talk about log management we refer to a precise process which consists of the centralized collection of data that comes from different operating environments such as: devices, databases, applications and much more. Logs are produced by various system events , many of which are particularly important in the business environment.
So let’s see some important details regarding log management.

The importance of collection-in-log-management
The procedure for collecting log data is important to achieve various objectives at the company level. The main ones are: to verify the vulnerability; manage possible security problems; control access to data and applications; the monitoring in real time ; check for any malfunctions at the application level.
From a regulatory point of view, then, log management is very important at a company level as allows you to observe the most important principles concerning data protection . This is established by the “EU 95/46 / EC” directive. It is also required by the obligations established by the “ General Data Protection Regulation (RGPD or GDPR) “.
Hence, these features illustrate how important good log management is and how it can help companies prevent potentially invasive events before they occur.
This type of action corresponds to what, in jargon, is called “Privacy by Design”. According to this principle, it becomes necessary to execute the right strategies to avoid creating risks and problems related to violations.
The-problems-to-face-in-log-management
Log management needs the correct balance between the dynamic availability of resources and the growing number of log data . In addition, from the first step of acquiring the log data, it is appropriate to consider several elements. These often generate various complexities such as, for example: the quantity of sources to be taken into account; the number of data logs created; the multiplicity of events that give life to data log ; the types of data log ; the method of acquiring the data logs ; the compliance of the data log protection systems.
Log management needs the correct balance between the dynamic availability of resources and the growing number of log data . In addition, from the first step of acquiring the log data, it is appropriate to consider several elements. These often generate various complexities such as, for example: the quantity of sources to be taken into account; the number of data logs created; the multiplicity of events that give life to data log ; the types of data log ; the method of acquiring the data logs ; the compliance of the data log protection systems.
It is therefore advisable to plan the strategies that allow you to adopt the right solutions for your log management staff. In this way, technicians will be able to intervene while respecting the requirements already mentioned.
The characteristics of a log-management infrastructure
The infrastructure for log management is formed by the union of hardware, software and network elements that are set up so that they can communicate effectively with each other. The communications between these components are made within the same network that is used for the common activities of the company.
Nevertheless, for a company it is also important to take into account the possibility of collecting data using a different network so that any spyware attacks or other incidents will alter, intercept or delete the data.
If from the logistical and architectural point of view it is not possible, in a company, to carry out this second possibility, alternative measures should be adopted such as, for example, data encryption.
Summarizing, therefore, a log management infrastructure should ensure compliance with the following requirements: maintaining information that serves to achieve the collection objective following the principles of “minimization” and “proportionality” ; ensure that data remain unalterable throughout their life span; ensure the integrity of the data collected without making changes; keep the data for a limited period of time.
The data-aggregation at the company-level
As companies grow and reach large numbers of applications within their environment, data collection becomes an increasingly important and decisive challenge.
In addition, if we take into account the difficulty of collecting sufficient data logs to be able to remain compliant, respect for privacy standards and security issues that arise from modern threats, we easily realize how the collection becomes an increasingly complex challenge.
So, at the enterprise level, the key to creating an efficient collection system is the ability to dynamically capture data in real time from all available sources. Have a solution that allows you to put your data in a central location, such as a data lake , and facilitate filtering , transformation, classification, allows you to make the log management task easier for the company.
SOCaaS and the advanced log management system
A very advanced solution is the one offered by the SOCaaS , in particular by its component SIEM , which leverages the innovation of artificial intelligence. This allows you to analyze the data collected so as to find possible suspicious data.
In addition, a qualified technical intervention is always made available at any time of the day with precise and non-distracting tasks. The intervention allows you to verify the alarm notifications that are generated by the system so as to exclude false positives , intervening to eliminate the threat and give constant reports over time .
The ever increasing data collection and the analysis of artificial intelligence allow to make the service very convenient and complete.
The potential of the SOCaaS-system for companies
As we have just seen, it is very convenient for companies to rely on a SOC service (SOCaaS). The greatest potential is represented precisely by the innovation brought about by artificial intelligence that allows you to achieve maximum results regarding the constant and continuous analysis of data so that it has the certainty of identifying possible threats in a very short time . Thanks to this system, therefore, risks will be prevented and mitigated.
An added value, then, is not having to hire specialized technicians with specific skills in identifying and verifying threats. Those who rely on this service will also be able to receive reports on the situation and notifications in case of problems.
SOCaaS, therefore, allows you to take the right precautions against those still unknown techniques and has the ability to find the link between data concerning possible attacks with still unknown systems. This is thanks to the analysis of user behavior and infrastructure intities ( UEBA ).
In addition, the structure of the system is designed to bring about constant improvement. The synergistic work between technicians and artificial intelligence allows us to identify even unconventional breach attempts.
For companies it means improving their defenses by adapting them based on the data collected previously.
SOCaaS is perfect for those companies that want to work safely using network-based infrastructures. This is a guarantee of defense against cyber attacks .

The-advantages of choosing our SOCaaS for log-management
Choosing to rely on our SOCaaS has several benefits.
The first is to save money in both the short and long term. In fact, you will avoid buying dedicated hardware and specific software . Plus, you won’t even need to hire new employees or upgrade the skills of those who already work.
Another benefit is having the professional support of technicians who update every day to have the skills to fight new types of threats. This type of assistance is priceless and it is extremely difficult to obtain within the company staff. This is also due to the current shortage of professionals in the sector.
A further advantage is to have always updated technology available . You will not have to worry and worry about always updating the software, because these, solely responsible for the collection of data for SOCaaS, are always kept to the latest version.
Do you want to get more information to learn more about the SOCaaS functionality of SOD? Contact us to find out how we can help you keep your company’s defenses up.
Useful links:

Cyberattacks are numerous and do not distinguish between companies and individuals when targeting a target. You’ve most likely heard the term “cyber threat” in the media before, but what exactly are we talking about? Other ways you may have heard this are “cyberthreat”, “cyberattack” or similar.

What is a Cyber Threat?
Today the term “cyber threat” is used predominantly in the world of information security.
A cyber threat is a malicious act conceived with the purpose of damaging systems, stealing data or any purpose that has the purpose of causing damage of any kind. Viruses, data breaches and DDoS attacks are included. Even if the threat is virtual, what is real is the attacker’s intent as well as the potential impact. While many cyberattacks are mere nuisances, some are quite serious. Some even potentially threaten human lives.
The potential impact that these kinds of attacks can have is often underestimated. Most of the time, the attacks are easily identifiable and do not pose much risk. Instead, other times it happens to come across some more sophisticated threats, difficult to identify, which represent a big problem even for many companies.
Cyber threats are a major concern for businesses. Cyberattacks can lead to power outages, government equipment failures, and breaches of state secrets. They can manipulate telephone and computer networks or, as in the case of ransomware, they can cripple entire systems by making data inaccessible.
Every day new companies and organizations set foot in the digital world with awareness of the risks associated with their technological infrastructures. In some cases, cyber threats are underestimated and this often means great economic and image damage for the company that has underestimated cyber threats and security.
The increase in IT-related risks is real, as are data security solutions. The best thing to do is to take the necessary safety measures right away.
Types of Cyber Threats
The types of cyber threats are numerous, and it must also be considered that they are constantly evolving. The intent of hackers is usually to secure an economic gain by carrying out sabotage, espionage or data theft operations. As a result, they can be expected to do everything possible to achieve their ends.
Virtually every cyber threat falls into one of the following ten types of risks. Hackers have an abundance of options to choose from in order to operate. Furthermore, computer literacy is all in all poor, so hackers often have an easy time, especially for small local realities.
The 10 most common types of computer threats
Malware
It is a type of software that executes a malicious command on a device or within a computer network, corrupting data or taking control of the system.
Phishing
Phishing is an e-mail attack that consists of tricking the recipient into revealing confidential information or inviting him to download malware by clicking on a link in the body of the message. These are real scams, which we have talked about extensively in other articles. Often they don’t even involve great IT skills on the part of the attacker, just a little social engineering.
Vishing
Vishing is a more sophisticated form of phishing in which the hacker uses VoIP technology to contact the victim, attempting to trick them. There is also a variant that instead uses text messages to attack, it is called smishing.
Man in the Middle
As the name suggests, this type of attack refers to when a hacker intervenes in a conversation posing as one of the two parties, with the aim of stealing sensitive information. What we often don’t think about is that the conversation is between two machines and therefore not immediate to monitor.
Trojan viruses
The origin of its name is inspired by the famous Trojan Horse of ancient Greece. Trojan is a type of malware that infiltrates a computer system by hiding its true nature. For example, it could impersonate known software and then release malicious code once inside the host device.
Ransomware
Ransomware is an attack that uses encryption to make information on a system inaccessible. The aim is to demand a ransom in exchange for being able to access the data again. Possibilità che a volte, in realtà, non è nemmeno assicurata.
DDoS attack
It occurs when the attacker uses many devices to overload a target, such as a website, with requests, causing it to crash or become instabilities.
Attacks on IoT devices
This is an increasingly popular attack due to the nature of the targets. Devices such as sensors or industrial plants connected to the network are vulnerable to multiple types of cyber threats. The hacker could take control of the device and then later use it in a DDoS attack. Alternatively it could steal the information present in the device itself obtaining important data to continue the attack. Given their number of frequently out-of-date operating systems, IoT devices are a very attractive target.
Malware in mobile applications
Phones and tablets are just as vulnerable to malware as any other device. È possibile inserire malware all’interno di app, nei siti web o nelle e-mail sfruttando il phishing. Once compromised, a mobile device can provide access to personal information, location data, and financial accounts.
A recent example of this type of eventuality is Pegasus software, which is used to monitor and collect data from journalists around the world. (Source: The Guardian)
Practical defense and prevention solutions
Cyber threats are always expanding and improving. Millions of them are created every year, many of them follow the aforementioned characteristics, but others are technologically more complex and more powerful.
Fortunately, however, there are also more and more highly qualified companies in the field of IT security that offer cutting-edge tools and services that help prevent, identify and promptly block all kinds of IT attacks.
Threat detection tools
Threat detection tools are an essential part of a company’s cybersecurity technology stack. Threat detection is also the first defense against any Cyber Threat.
Specific solutions, such as the use of a SOCaaS, for example, are of vital importance for safeguarding an IT infrastructure, thanks also to the integration of the SIEM engine which includes UBA and UEBA, guaranteeing complete control also over the users.
Another useful tool is definitely ACP. Acronis Cyber Protect is a solution that integrates data protection and management to safeguard your endpoints, data and systems. Its automation capabilities provide unparalleled protection, enabling businesses to increase their productivity and reduce risk.
Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Test (VA-PT)
Services like VA & PT are field tests that test the infrastructure in a concrete context. Our teams of white hat hackers find vulnerabilities within the system to point the finger at weaknesses to fix.

Conclusions
We have learned what a cyber threat is and its most common types, also discovering which solutions can be adopted in order to guarantee better corporate and employee safety.
What countermeasures has your company taken to protect your safety? If you would like more information about it, you can contact us by pressing the button below. We offer ad hoc services and solutions to strengthen corporate defenses.
Useful links

Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Every year the number of attacks that threaten the security of devices, computer systems, servers and network infrastructures is growing steadily. This is done by taking advantage of the vulnerabilities present in these systems. Among the many types of attacks, particular attention must be paid to the pass the ticket (PTT) attack.
With a pass the ticket attack it is possible to take advantage of the Kerberos network protocol, present in all major operating systems, to access a user’s session without having his login credentials. An attack of this type can be difficult to detect and is usually able to bypass the most common system access controls.

Pass The Ticket: what it is and how it works
Kerberos
Before understanding in detail what a PTT attack is and how it works, it is advisable to clarify the Kerberos network protocol since an attack of this type uses this protocol. Kerberos is a network protocol designed by MIT in the 1980s and became a standard IETF in 1993. It is used for strong authentication between different terminals through a symmetric key encryption system, without transmitting any passwords.
The advantage of using the Kerberos protocol lies in its strong authentication system between client and server. This makes it very effective against phishing and “ man in the middle ” attacks.
Kerberos is integrated into all major operating systems belonging to well-known companies such as Microsoft, Apple, Red Hat Linux and many more.
With a pass the ticket attack it is possible to exploit Kerberos authentication to gain access to a user account. The consequences that such an event could entail are not are to be underestimated. Among the many imaginable scenarios, for example, there could be the possibility that the compromised account enjoys high administrative privileges thus guaranteeing the hacker full access to resources.
The attack
A pass the ticket attack allows you to gain privileged access to network resources without having to use any user passwords . Here’s how: In Active Directory, a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) serves to prove that a user is just who he says to be. Through some tools and techniques, a hacker could collect these tickets and use them to request Ticket Granting Services (TGS) in order to access resources present in other parts of the network.
A PTT attack could involve risks even if the compromised account does not have particular administrative privileges since the hacker, through the Lateral Movement, may be able to gain access to other accounts and devices.
The difference between pass the ticket and an attack pass the hash lies in the fact that the former exploits TGT tickets that have an expiration of a few hours, while the latter uses NTLM hashes that change only in case a user decides to change his password. A TGT ticket must be used within its expiration time or renewed for a longer period of time.
How to Defend and Prevent a Pass The Ticket Attack
Keeping a network and the devices connected to it safe is a very important factor. You must always have protocols and software that are able to guarantee effective protection from all kinds of threats , with up-to-date systems that keep sensitive information safe. Enterprises can take advantage of endpoint detection and response technologies. Local detection of multiple tickets used for the same session will be possible.
Account case without-privileges
In the event of a pass the ticket attack, if the compressed account from which the TGT or TGS was stolen was a low-privilege account, the mitigation could be quite simple. Just reset the user’s Active Directory password. Such an action would invalidate the TGT or TGS, preventing the hacker from generating new tickets.
Case-account with privileges
Conversely, if the PTT attack compromised a privileged account, limiting the damage is much more difficult. In these cases, companies could respond to the attack by resetting the Kerberos TGT service to to generate a new signing key, making sure to delete the compromised key.
Next you need to drill down into Kerberos logs and Active Directory information to investigate and find out which network resources have been compromised. In this way it is also possible to understand which data may have been stolen. The technology SIEM allows organizations to assimilate, analyze and analyze this data.

Protection from attack
To ensure complete protection of an infrastructure, also preventing pass the ticket attacks, it is good to use valid detection technologies such as UEBA and SIEM. In fact, it is possible to prevent Pass The Ticket attacks by analyzing the behavior of users and entities. The solution UEBA , in these cases, would ensure the quick identification of any compromised account, blocking it in order to mitigate the damage.
Some software SIEM also allow not only to analyze traditional logs but are also able to provide an accurate analysis of security , analyzing the behavior of the network and users in order to detect promptly the presence of any threats to the infrastructure.
Conclusions
We have seen what a pass the ticket attack is and how companies can adopt specific solutions to intercept the dangers and anomalies of an entire IT infrastructure. This allows us to mitigate threats more effectively.
A complete solution, as we have seen, involves constant and granular communication monitoring . The solution we propose for this purpose is a SOCaaS .
If you want to know our dedicated security services, do not hesitate to contact us. You can use the button below, we will be happy to answer any of your questions.
Useful links:

Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Cyber Threat Analytics applications monitor security logs and the network to promptly detect any malware infections (for example, attacks zero day e i ransomware), the compromise of the system, the activities of “ lateral movement ”, pass-the-hash , pass-the-ticket and other advanced intrusion techniques. The use of a SOCaaS allows to extrapolate data from sources such as firewalls, proxies, VPN, IDS, DNS, endpoints, and from all devices connected to the network with the aim of identifying harmful models such as “beaconing”, connections to generated domains digitally, actions performed by robots and all anomalous behaviors.
Our system SOCaaS is equipped with artificial intelligence that enriches and transforms events SIEM, so you identify threats across your entire IT environment, including business-critical applications.
What are the-advantages at the enterprise-level?
The use of a SOCaaS. Below is a list with only some of the advantages that the use of SOCaaS can entail rapid detection of violations, reducing the impact of these. Additionally, a SOCaaS provides comprehensive threat responses and investigations, decreases monitoring and management costs, as well as compliance costs.
The use of a SOCaaS also allows you to receive quantified and non-subjective reports on threats and risks.

SOCaaS use cases
After a general overview of the advantages that the use of SOCaaS could offer to the company, let’s see in what contexts it is normally used .
A SOCaaS consists of elements that are very suitable to be applied in case of abnormal execution of applications, as well as in the analysis of bot traffic to a malicious website.
In other cases, SOCaaS identifies unusual DNS queries, a possible remote command and control activity, analyzes the spikes in bytes to external destinations and then also checks the traffic, relating it in an application / port context.
Other scenarios in which the use of SOCaaS is ideal are the detections of exploits, sessions of unusual duration, but also connections to IPs or blacklisted domains and anomalous activity in general.
Finally, it can also detect targeted SPAM attacks and phishing attempts.
Threat Models
By analyzing threat indicators it is possible to detect correlated behaviors on multiple data sources, to also detect all those threats that usually go unnoticed. Multiple threat indicators occurring in a scheme and involving similar entities tend to present a greater risk of posing a real threat.
The Threat Models define these patterns and combine threat policies and indicators to detect related behaviors across multiple data sources, identifying threats that may go unnoticed. Below are some of the more common Threat Models that are included in the use of a SOCaaS
Lateral Movement Detection
This Threat Model detects the possible scenarios of “ lateral movement “, used by attackers to progressively spread across a network in search of key resources and data. The signs of such an attack can be varied and we can divide them into three categories: Abnormal authentication, suspicious privileges, abnormal process.
Abnormal authentication is usually detectable by some clues. For example if an account accesses a host that has never been reached before. Or if explicit credentials are used on multiple hosts, or if a suspicious authentication type / process is detected.
Concerning suspicious privileges, here are some indicators detectable with the use of a SOCaaS:
- abnormal provisioning activity
- suspicious escalation of privileges
- abnormal access to network share objects
An abnormal process is detected in this way through the use of a SOCaaS: an unusual process code, or the suspicious creation of scheduled tasks. Alternatively, suspicious changes to the registry settings may be detected.
Detection of compromised hosts
This model is employed in the use of SOCaaS to detect hosts showing signs of infection and compromise by relating host and network based anomalies to the same entity.
A possible alarm is given by anomalies in outgoing traffic . This occurs when traffic goes to random domains or known malicious hosts. In other cases, however, an abnormal number of domains contacted is another alarm bell detectable through the use of a SOCaaS.
anomalies in the endpoint are found when rare processes or suspicious use of ports or protocols by the process itself are found. One possibility is also to detect an unusual agent.
APT detection using a SOCaaS
Detection APT detects attacks on health care networks , where the attacker’s aim is usually to obtain a unauthorized access to a network with the intention of remaining undetected for an extended period.
This includes phishing attempts , detection of a network scan or circumvention of controls. In the delivery phase, however, traffic to random domains, an anomaly in DHCP traffic or traffic destined to known malicious hosts may be identified.
During an exploit , the indicators can be: the detection of activity from terminated accounts, anomalous DNS traffic, but also a suspicious authentication process. Another possible indicator identifiable with the use of SOCaaS is an anomaly in the speed of the network.
Through the use of a SOCaaS, cases of data exfiltration can also be detected. The signals in this case are l ‘Unauthorized upload of data over the network.
Detection model Phishing using SOCaaS
This model is able to detect possible phishing attempts towards users within the organization . We’ve talked about it in other articles as well, and here are some indicators of this type of attack. A wake-up call is definitely the detection of known phishing campaigns. It is also not uncommon for spear phishing attacks to be detected.
The use of a SOCaaS is also able to identify possible phishing attempts or persistent phishing campaigns, thanks to the comparison with emails from senders / domains / IP addresses known in the blacklists. As usual, beware of suspicious email attachments, but the use of a SOCaaS could automate, at least in part, the checks.
It is then possible to identify outbound traffic anomalies , for example that towards random domains, which is also a possible phishing signal. Classic traffic to malicious hosts, an abnormal number of rare domains accessed, can also be indicators.

Host / Account Enumeration on LDAP
Usually used to identify potential assets or account enumerations on the network by malicious entities.
Running suspicious processes
- Abnormal process / MD5 detected
- Use of possible sets of AD (Active Directory) enumeration tools
- Detected use of malicious tools and utilities
Network scanning
- Possible AD accounts / enumeration privileges
- LDAP or SMB service count
- Abnormal number of Kerberos service ticket requests
- Port scanning
Authentication anomalies
- Accounts accessing a host for the first time
- Using never-before-seen accounts on the network
- Abnormal number of failed authentication requests
Reconnaissance followed by potential exploitation
This threat model aims to identify successful network reconnaissance attempts, followed by indicators of exploitation.
External scanning
- Scanning ports from external hosts
- Enumerating hosts from external hosts
Network scanning
- Possible count of AD accounts / privileges
- Enumeration of LDAP services
- Unsolved number of Kerberos service ticket requests
- Spikes in traffic LDAP
- Enumeration of SMB services
Anomalies in processes
- Detection of abnormal processes or MD5
- Suspicious creation of scheduled tasks
- Suspicious changes to registry settings detected
Conclusions
We have seen what are the major SOCaaS use cases, taking a look at some of the most common threat models that it includes in its protection system. For information on malware threat patterns and threat identifiers visit this article.
Using a SOCaaS is a solid and highly valuable business solution, ask us what it can do for your business, we will be happy to answer any questions.
Useful links:

Tempo di lettura stimato: 7 minutes
Quando parliamo di “left of boom” o “right of boom” ci riferiamo ad un concetto che all’apparenza può sembrare superficiale. Invece, è un potente strumento che offre la possibilità di analizzare i conflitti di sicurezza sia da un punto di vista offensivo che da uno difensivo. In una ipotetica linea temporale di un attacco, ciò che si trova alla sua sinistra (left of boom) si riferisce a quello che accade prima. Analogamente, ciò che sta alla destra, è quello che avviene dopo.
Nel linguaggio comune molto spesso anziché “boom” si utilizza il termine “bang”, ma il significato resta comunque invariato. Si tratta, in sostanza, dell’evento stesso intorno al quale si analizza il periodo precedente e successivo.
Quindi, “left of boom” è l’insieme di eventi che si verificano prima dell’attacco. “Right of boom”, invece, è l’insieme di eventi che seguono il “boom”. Questa è la differenza sostanziale tra i due termini. Se le azioni difensive riescono a rilevare gli eventi nel periodo “left of boom”, è possibile trovare e adottare soluzioni per prevedere quando accadrà il “boom”.
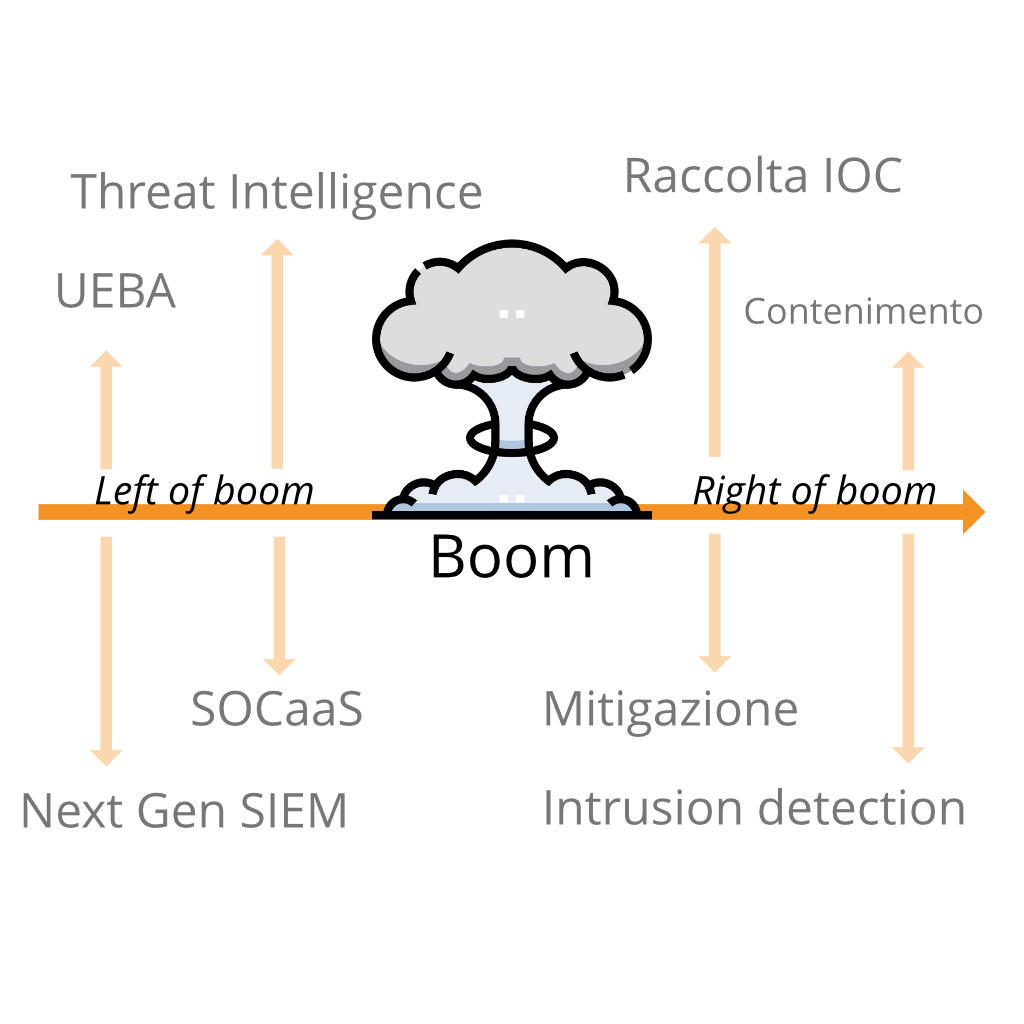
Per una persona inesperta nell’ambito della sicurezza informatica, questi concetti riguardanti la linea temporale di un attacco informatico potrebbero non essere nemmeno presi in considerazione, per questo motivo molte aziende preferiscono avvalersi di un SOCaaS.
Left of Boom
Un buon penetration tester riesce a rilevare alcuni eventi di tipo “left of boom”, ma spesso si tralascia la raccolta di informazioni sulle minacce. Certe volte non è in grado di distinguere tra loro concetti come “ingegneria della sicurezza, scoperta e risoluzione delle vulnerabilità” da un “controllo di prevenzione automatizzato”.
Non esiste in realtà un vero strumento valido di prevenzione, più che altro i controlli di sicurezza sono controlli di rilevamento. Alcuni di questi controlli integrano dei meccanismi di risposta automatizzati che impediscono il susseguirsi di spiacevoli eventi.
Un’applicazione web che previene attacchi di tipo XSS o SQLI è davvero utile per rilevare input non validi e risponde scartando il contenuto prima che l’iniezione possa verificarsi.
Un firewall progettato per bloccare le porte rileva semplicemente il traffico indesiderato in relazione al protocollo usato per la connessione e al numero della porta verso la quale si desidera accedere, interrompendo e reimpostando la richiesta di connessione.
Questi esempi si legano bene al concetto di “right of boom”. I controlli di prevenzione rilevano il “boom”, l’evento, e rispondono immediatamente arginando i possibili danni. “Left of boom” e “right of boom” sono così vicini nella linea temporale che sono difficilmente distinguibili, fino a quando non si esegue un’analisi accurata degli eventi.
Questo è uno dei motivi per cui i professionisti, nell’ambito della sicurezza informatica, amano i controlli di prevenzione. Lavorano rapidamente per correggere gli errori prima che gli hacker riescano a raggiungere i loro obbiettivi, limitando i danni.
Un SOCaaS in questi casi è una delle soluzioni migliori da adottare per proteggere l’integrità di un sistema informatico.
Right of Boom
Generalmente minore è la distanza tra “right of boom” e il tempo di risposta ad una minaccia, minori sono le conseguenze provocate da un eventuale attacco informatico. Ovviamente questa è solo una considerazione logica, non vale come regola assoluta.
Per alcune violazioni, la linea temporale tra l’evento e l’eliminazione completa della minaccia è discutibile, poiché il rilevamento è avvenuto dopo che l’hacker ha raggiunto il suo obbiettivo. Se gli hacker riescono ad infiltrarsi nel sistema ma vengono fermati in tempo, non arrecando nessun danno all’infrastruttura. In questo secondo caso, quindi, non c’è il “boom” di cui stiamo parlando.
Un esempio di right of boom
Per spiegare meglio il concetto di “right of boom” potremmo prendere come esempio un comune “malware”. I malware generalmente vengono sviluppati per attaccare in massa molti dispositivi, senza tanta discrezione. Con “right of boom” ci riferiamo a quel periodo di tempo che è passato da quando è avvenuta l’infezione da parte del malware.
Se hai letto gli altri articoli pubblicati da noi avrai appreso come gli hacker utilizzano queste tipologie di infezioni allo scopo di raccogliere informazioni sensibili, che vengono rivendute ad un terzo soggetto. Se il “right of boom” è più breve del tempo che l’hacker impiega per vendere queste informazioni, il danno può essere contenuto.
I migliori sistemi di sicurezza riescono ad accorciare il tempo “right of boom” riuscendo a raccogliere informazioni sugli attaccanti nel “left of boom”. Ci si può riuscire implementando delle contromisure in base al modello di minaccia. Questi strumenti permettono di scansionare intere infrastrutture, osservando i nuovi indicatori di minaccia giorni o addirittura settimane prima che gli attacchi si distribuiscano.
Come abbiamo visto anche in altri articoli, non sempre gli attacchi si svolgono in breve tempo. È, anzi, più probabile che gli hacker coinvolti agiscano in un primo, lento, periodo solo per raccogliere le informazioni necessario per sferrare l’attacco. Nel periodo “right of boom”, tornano utili strumenti come la cyber threat intelligence e un team di threat hunting.

Perché sono importanti i concetti “Right e Left of boom”
Se ci mettessimo nell’ottica dell’hacker, il concetto di “right of boom” e di “left of boom” può aiutare a decidere quale schema d’azione sia meglio intraprendere.
Supponiamo il caso in cui un hacker abbia a disposizione due metodi per potersi introdurre in un sistema informatico. Se uno dei due metodi potrebbe venire rilevato nel periodo “left of boom”, invece l’altro nel “right of boom”, è ovvio che l’hacker preferirà il secondo. Infatti, questo garantirebbe maggiori probabilità di successo dell’attacco.
Analogamente, tra due metodi che possono essere rilevati “right of boom” si sceglie quello che ha più possibilità di venir scoperto in ritardo. Più tempo passa dal boom alla rilevazione, maggiori sono le probabilità di successo. Questo tipo di ragionamento è importante per determinare quale tattica ha una linea temporale più ampia.
Ragionare in quest’ottica non è affatto semplice, richiede delle conoscenze avanzate da parte dell’esperto di sicurezza. Richiede inoltre il dover prendere in considerazione tutte quelle ipotesi che potrebbero potenzialmente determinare il successo dell’hacker.
Velocità
Un hacker è in grado di riuscire a prevedere se, utilizzando determinate tattiche, riuscirebbe a raggiungere l’obbiettivo più velocemente rispetto all’esperto che cerca di rilevare gli attacchi. Il “boom” è il primo contatto, nell’insieme delle tattiche d’intrusione utilizzate per accedere illegalmente ad un sistema informatico. Le rimanenti tattiche si collocano prima e dopo di esso.
Velocità e furtività solitamente si annullano a vicenda. Infatti, molto spesso si può essere più veloci sacrificando parte della furtività.
Velocità e furtività non vanno molto d’accordo quando parliamo di attacchi informatici. Essere furtivi, evitando di lasciare tracce, richiede più attenzione e quindi inevitabilmente anche più tempo. Tuttavia se lo scopo di un hacker non è un singolo obbiettivo ma una serie di più obbiettivi, l’essere veloci può rivelarsi efficace.
Per difendersi dagli attacchi, è possibile raccogliere gli indicatori di compromissione (IOC) per rimediare alle vulnerabilità presenti e per introdurre nuovi controlli di rilevamento, rendendo più sicuro il sistema informatico.
Conclusioni
È importante conoscere il concetto di linea temporale degli attacchi e abbiamo visto come i concetti di “left of boom” e “right of boom” influenzino i meccanismi di risposta alle minacce di intrusione.
I concetti che abbiamo visto in questo articolo, nonostante non aggiungano niente di concreto alle tecniche di difesa o di attacco di un sistema, offrono un punto di vista. Nella continua lotta tra hacker e operatori di sicurezza, avere una strategia vincente significa non solo disporre di strumenti efficienti, ma anche pianificare in modo dettagliato ogni dettaglio, prima e dopo gli attacchi.
Per sapere come un SOCaaS può aiutarti a monitorare l’infrastruttura aziendale e cogliere gli indizi “left of boom”, non esitare a contattarci, sapremo rispondere a ogni domanda e ti offriremo una soluzione per la tua azienda.
Useful links:

Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
Today, facing an attack in a corporate SOC is very similar to being under attack without knowing which direction the blow is coming from. The threat intelligence can keep you informed of security issues. However, in many cases, this information is only provided when you are already under attack, and is rarely very useful except in retrospect. It would take a different approach to data analysis, and that’s exactly what we propose with predictive cybersecurity .
In cybersecurity, threat intelligence is still relied upon as a fundamental defensive tool. Unfortunately, threat intelligence only covers a subset of threats that have already been found, while attackers constantly innovate . This means that new malware executables, phishing domains and attack strategies are created all the time.
Threat intelligence has a strong value for reactive incident response. It helps when pivoting through an investigation, identifying intent or other useful data, and providing additional investigative assistance. But it has limited value for detection, as threat actors avoid reusing their attack infrastructure from one target to another.
If the clues you see are different from those known from previous attacks, what can you do to move forward with effective detection? A legitimate question, for which predictive cybersecurity perhaps has an answer.
… what if you could know what is going to hit?
SOCaaS: predictive cybersecurity
Eyes on opponents rather than past attacks
The SOCaaS solution offered by SOD brings predictive cybersecurity capabilities to cybersecurity. The solution maps adversaries , instead of threats, and analyzes their actions to predict the behavior and the tools used in their attacks.
The analytical engine translates behavioral patterns into profiles of adversary attack infrastructures , which indicate as ( trojan, phishing or other forms of attack ) and where ( branches, customers, partners, peers, industry and geographies ) < strong> attackers are planning to target your company .
This provides a preemptive attack map, which identifies opponents based on their attack phase and current position within the extended business landscape . But not only that, in fact, information about the opponent, typical attack patterns and possible countermeasures that can be taken in advance are also identified. This way you can cancel the threat before it materializes .

Predictive cybersecurity: understand what’s going to happen first
Our SOCaaS provides predictive detection capabilities against internal and external threats with the combination of user, entity and adversary behavior analysis. Our Next-Gen SIEM uses an analytics-driven approach to threat detection. SOC provides visibility in the crucial early stages of an attack. That is when cyber actors are targeting, planning and preparing the infrastructure for an attack.
With this level of predictive visibility, the team can prevent attacks and systematically contain those in progress. Predictive cybersecurity allows defenders to tune their systems against the attack infrastructure. In fact, it is possible to build blacklists that include the IP addresses and the host names of the instances used for the attack . Other measures include fortifying corporate systems against the specific malware that is used to target them, rendering the attack powerless when it occurs.
Opponent Behavior Analysis extends the capabilities of Next-Gen SIEM by continuously providing updated analysis of opponent information and behavior . This encompasses the entire attack infrastructure for dynamic and proactive threat protection.
SOCaaS automatically translates the pre-attack behavior of opponents into actions or countermeasures that can be taken against phishing, compromise of corporate email, ransomware, fraud and many other common threats.
Common use-cases
Threat-chaining
Correlate breaches from the same adversary / campaign into a cohesive threat, even if different pieces of attack infrastructure are used for each event.
Prevention and preventive defense
Preemptively blocking an opponent’s entire attack infrastructure, such as newly created phishing domains, for preemptive defense.
Strengthen vulnerable resources
Focus and secure the most vulnerable parts of your infrastructure based on information that identifies which areas are possible targets.

The information provided by SOCaaS is used to add more context to existing threats, as well as provide information on attacks that have not yet been implemented or are in the early stages, such as reconnaissance. This allows for direct action against evolving threats and a more robust defense.
Conclusions
Relying on luck to catch threats is madness, as the recent SolarWinds attack . Make your fortune with SOD’s SOCaaS solution, making sure you see threats before they happen and are “lucky” enough to counter them.
Useful links:

Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
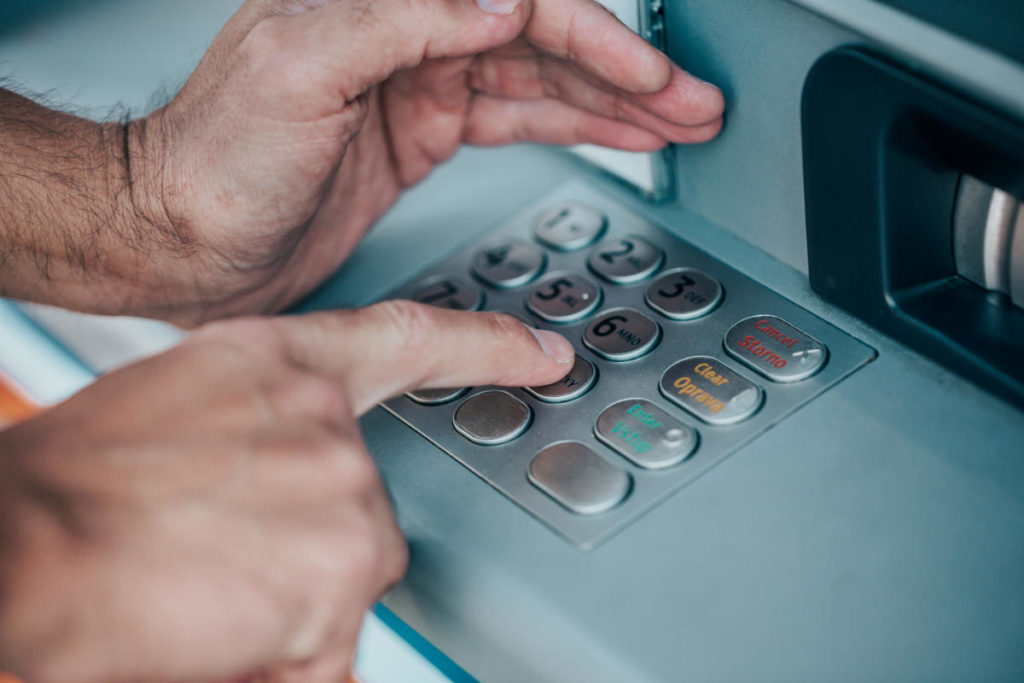
The term shoulder surfing might conjure up images of a little surfer on his shirt collar, but the reality is much more mundane. shoulder surfing is a criminal practice in which thieves steal your personal data by spying on you while using a laptop, ATM, public terminal or other electronic device among other people . This social engineering technique is a security risk that can cause disaster, especially if the stolen credentials are corporate.
The practice long predates smartphones and laptops and dates back to when criminals spied on pay phone users as they entered their calling card numbers to make calls . Many years have passed, but the technique has not been lost. Thieves have evolved to observe their victims typing their ATM PINs, paying at self-service petrol pumps, or even making a purchase in a store.
A similar technique for ATM theft involves a card cloning device superimposed on the card insertion hole and a micro camera to spy on the code. The micro camera performs an act of shoulder surfing . Card cloning is essential because without a physical device the pin is useless, but in the case of account credentials on the network, all you need is user and password.

When does Shoulder Surfing take place?
shoulder surfing can happen whenever you share personal information in a public place. This includes not only ATMs, coffee shops and POS devices in general, but virtually any place where you use a laptop, tablet or smartphone to enter personal data.
Long-time shoulder surfers did not usually loom behind their victims to scrutinize information. Instead, they stood at a safe distance and interpreted finger movements as people typed numbers on the keyboard . Similarly, today’s social engineers often escape attention as they quietly observe others in public places such as airport lounges and shopping malls, bars and restaurants, on trains or subways, or wherever there are people, to tell the truth.
Indeed, today’s most sophisticated criminals are watching from further away, hidden from view. They could use binoculars, micro cameras, or the camera of their phone or tablet to scan your screen or keyboard. Not only that, they may eavesdrop as you read credit card numbers on the phone or provide other sensitive information. Criminals could also take pictures, make a video or audio record of the information and then interpret it later.
Whatever the methodology, it is clear that technology has not only helped us to be more connected and be able to afford to pay for a frappuccino with our mobile phone, but it has also exposed us to security risks. When it comes to sensitive data, especially if there is a corporate account involved that could access other people’s sensitive data, you should never let your guard down , consequences could be very serious .
As shoulder surfing commonly happens
Before suggesting some methods to prevent shoulder surfing to be put into practice immediately, let’s take a closer look at how credential theft could happen with this technique.
At the bar or in the cafeteria
You’re in a busy restaurant bar waiting for a friend. To pass the time, you connect to Instagram. Unfortunately, you don’t notice that the person stuck in line next to you is looking at your password, which happens to be the same one you use for your email and bank account.
At the ATM
You’re taking cash at an ATM. You feel safe because the man after you in line is at least 10 feet away and is even looking at his phone. In fact, he is recording your finger movements on his phone and will later decrypt them to get your PIN number.
To the airport
Your flight is delayed, so grab your laptop and kill your time by reading a couple of work emails to keep up to date. Log in to the company website to read your mail and enter your username and password. You are so calm that you don’t see the woman a few places away as she stares at the screen while you enter data.

What are the consequences of shoulder surfing?
Using your credit card information to make fraudulent purchases is just one example of the damage you could suffer if you fall victim to shoulder surfing . The more personal information a criminal captures about you, the more serious the consequences can be for your bank account and financial health.
A serious case of shoulder surfing can expose you to identity theft . A criminal could use your personal information, such as your social security number, to open new bank accounts, apply for loans, rent apartments, or apply for a job under your name. An identity thief could get their hands on your tax refund, use your name to get medical treatment, or even apply for government benefits in your name. They could also commit a crime and provide your personal information when questioned by the police, leaving you with a dirty record or arrest warrant.
Of course, if you suspect this has happened, you’ll need to go to the police immediately, block your checking accounts and notify the bank. If fraudulent actions have already been carried out in your name, you may need to prove that you are not involved.
Things get dangerous if the stolen data is from a corporate account. In fact, with the use of valid credentials, anyone could enter the company’s system and perform all kinds of actions, such as collecting additional data, placing malware, running a ransomware , steal customer data and then sell it online.
How to defend yourself from shoulder surfing
Two levels of protection can be identified, the first is proactive and is aimed at preventing credentials from being exposed to malicious people, the second is active and provides software to detect attempts to use stolen credentials.

Defend yourself proactively
If you really can’t avoid entering sensitive data on your laptop, tablet or smartphone in a public place, you should follow the countermeasures listed below.
Tip 1: Before entering any sensitive data, find a safe place . Make sure you sit with your back to the wall. This is the best way to protect yourself from prying eyes. Avoid public transport, the central armchairs of a waiting room and places where there is a lot of people coming and going.
Tip 2: Use a privacy filter. This hardware device is a simple polarized translucent sheet that is placed over the screen. It will make your screen look black to anyone looking at it from any unnatural angle . This will make it much more difficult for unauthorized people to see your information.
Tip 3: Two-factor authentication requires a user to prove their identity using two different authentication components that are independent of each other. Since this type of authentication only passes when both factors are used correctly in combination, the security measure is particularly effective. For example, this method is often used a lot in online banking. There are many services that allow you to use your mobile phone as a second authentication factor . This is done through special apps.
Tip 4: Another solution is to use a password manager . By doing so, you no longer have to enter each password individually on your computer. The password manager will do this for you after you enter your master password . This prevents unauthorized people from using your keyboard to determine the real password, provided that you properly protect your master password .
Actively defend yourself with a SOC and behavior analysis
Now let’s imagine that the corporate account credentials have been stolen. At this point only a behavior control system can trigger an alarm and therefore block the user before there is any damage.
In fact, using correct credentials, a normal traditional SIEM would not trigger any alarms. For an older generation SIEM, access would be legitimate, because the credentials are correct. The attacker would have free undisturbed access to the system and could continue with his attack plan.
With SOD’s SOCaaS service, however, abnormal access would trigger an alarm. The SOC provided is equipped with a Next Generation SIEM and a system UEBA control behavior . This means that any deviation from the user’s usual behavior would be reported.
In the case of credential theft, as happens with shoulder surfing, the access made by the attacker would therefore trigger an alarm because something is wrong . For example, the login could take place at anomalous times, in another country / IP, from a different operating system, etc.
Conclusions
shoulder surfing is a social engineering technique that focuses on user carelessness while entering sensitive data into a system. In the event that a user’s corporate credentials are stolen, the only really efficient thing is to have a system that analyzes user behavior and reports whenever suspicious actions are detected.
If you want to know in detail how a SOC and UEBA system can help your company defend against social engineering attacks, do not hesitate to contact us, we will be happy to answer any questions.
Useful links:

Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Una logic bomb, chiamata anche slug code, è un pezzo di codice inserito in un’applicazione, virus o malware che implementa una funzione dannosa dopo un certo limite di tempo o in condizioni specifiche.
Queste “bombe” sono spesso usate tramite virus, worm e Trojan per gestire al meglio il tempo a disposizione e fare il massimo danno prima di essere notati. Eseguono azioni come corrompere o alterare i dati, riformattare un disco rigido e cancellare file importanti.
In questo articolo voglio spiegare cosa sia un bomba logica e offrire qualche suggerimento per prevenirne i danni.

Cos’è un logic bomb virus?
Una bomba logica è spesso inserita in un virus o comunque in un file eseguibile. È composta da un codice malevolo che innesca un attacco quando vengono soddisfatte condizioni specifiche. Le condizioni possono essere positive (qualcosa che accade) oppure negative (qualcosa che non accade). Nel primo caso un esempio è quello dell’apertura di un programma, invece, un esempio di condizione negativa è un utente che non compie il login.
Le bombe logiche sono spesso installate da qualcuno con un accesso di alto livello, come un amministratore di sistema. Tale persona può causare il caos impostando questi codici su più sistemi e programmandoli per “esplodere” simultaneamente quando si verifica un certo evento. Per esempio, potrebbero azionarsi quando un certo dipendente viene rimosso dal database degli stipendiati, cioè quando viene licenziato.
Con il termine slag code ci si riferisce al codice manipolato che rende dannoso un programma altrimenti sicuro. Le versioni a tempo di bomba logica sono quelle più diffuse e utilizzano come condizione positiva il trascorrere di un certo lasso di tempo.
Qualunque sia il nome usato, il metodo di attacco è sempre chiaramente lo stesso: il codice rimane dormiente nel software infetto fino a quando non viene innescato. Gli attacchi comuni coinvolgono la corruzione dei dati, la cancellazione dei file e la cancellazione dei dischi rigidi.
Come funziona
Il modo in cui una logic bomb funziona dipende da chi l’ha ideata. Ogni bomba logica è unica, ed è per questo che sono difficili da tracciare. Di solito sono personalizzate per essere il meno rilevabili possibile. Spesso sono travestite per sembrare un tipico virus informatico o inserite in altri tipi di malware come i worm. Worm e virus sono diversi, ma le bombe logiche non si preoccupano della distinzione: possono causare danni attraverso entrambi.
Una bomba logica è effettivamente un malware? Poiché fanno parte di altri programmi, no, ma di solito hanno un intento maligno. Ecco perché gli slag code sono così difficili da rilevare. Inoltre, essendo “solo” codice, potenzialmente inseribile ovunque, mitigare il rischio è più complicato.
La cosa migliore da fare, come utente finale che potrebbe essere coinvolto in un attacco con una logic bomb, è quello di tenere gli occhi aperti e chiedere agli esperti IT della tua azienda di fare i controlli necessari in caso di dubbio. Il rischio è quello di far scattare la bomba involontariamente cercando di trovarla.
Esempi di attacchi
Le bombe logiche possono cambiare in modo impercettibile un frammento di codice in modo che appaia tecnicamente normale ad un sistema automatico di ricerca delle minacce, mentre sembrerebbe molto sospetto per un occhio umano. Nel 2016, un programmatore freelance ha volontariamente causato un malfunzionamento ricorrente dei fogli di calcolo in una filiale della società Siemens. La filiale lo ha continuato ad assumere per risolvere il problema che lui stesso aveva causato (Fonte). In questo caso, i dipendenti non sospettavano nulla fino a quando una fortunata coincidenza ha costretto il codice maligno a uscire allo scoperto.
Anche le aziende possono usare bombe logiche per violare i propri clienti. Nel 2005, Sony fu coinvolta in uno scandalo per aver rilasciato dei CD che scatenavano una bomba logica quando venivano inseriti in un computer. Lo slag code contenuti nei CD installava un rootkit che bloccava la capacità del PC di copiare i CD. (Fonte)
Un altro caso di alto profilo si è verificato nei primi anni 2000, quando un dipendente di UBS Global, arrabbiato per una disputa salariale, ha piazzato una bomba logica a tempo che ha causato più di tre milioni di dollari di danni. Un segno evidente che uno snippet di codice molto piccolo può causare una grande quantità di danni. (Fonte)
Nel 2013, un attacco con una bomba a tempo in Corea del Sud ha cancellato i dischi rigidi di diverse banche e società di trasmissione. Il gruppo responsabile dell’attacco ha messo la bomba a tempo all’interno di un malware che ha finito per infettare oltre 32.000 sistemi. Le bombe sono esplose tutte insieme, causando il caos in tutto il paese. (Fonte)

Da dove vengono e come prevenire le logic bomb
Come abbiamo visto anche negli esempi, le bombe logiche sono tipicamente distribuite all’interno di una rete chiusa, come quella di un’azienda o di una filiale. Una delle probabili fonti è un dipendente scontento con accessi di amministratore, quindi un attento monitoraggio delle attività in uscita del personale dovrebbe rivelare qualsiasi attività sospetta. Ma non è tutto, le bombe logiche possono anche essere piazzate in allegati di email e download di file sospetti, quindi gli utenti dovrebbero essere vigili quando scelgono i file da scaricare.
Come abbiamo visto quando abbiamo parlato di phishing e di ingegneria sociale, la parte più hackerabile di un sistema, sono spesso gli user. Per questo una campagna preventiva è sempre un’ottima scelta. Prendersi cura del personale significa anche proporre dei training specifici tramite servizi di phishing etico.
Oltre alla prevenzione, è bene limitare i privilegi amministrativi a un gruppo selezionato di dipendenti in modo che sia meno probabile che qualcuno possa causare gravi danni alla rete con una bomba logica. Questo metodo preventivo, inoltre, riduce il numero dei sospetti in caso di attacco, rendendo l’appartenenza a quello specifico gruppo di dipendenti di per sé un deterrente contro gli attacchi interni.
La soluzione proposta da SOD
Dove la prevenzione fallisce e vincono invece gli hacker, è il campo ideale per implementare sistemi avanzati di monitoring e analisi.
SOD offre, per esempio, un sistema SIEM nella soluzione SOC as a Service. Tramite il SIEM vengono costantemente raccolte informazioni su quello che succede nella rete. Queste informazioni vengono poi arricchite con metadati contestuali per uniformarle e gestirle al meglio. Già questo è in grado di far scattare allarmi se alcuni eventi sospetti si verificassero. Ma se questo non bastasse, il SOC dispone anche di uno strumento di “User and Entity Behavior Analysis” (UEBA) che analizza il comportamento degli utenti e grazie all’interazione di una IA riesce a individuare comportamenti sospetti.
Se vuoi saperne di più riguardo al servizio SOC offerto, o se hai delle domande su come SOD può aiutarti a mantenere la tua azienda al sicuro, non esitare a contattarci. Saremo lieti di rispondere a ogni dubbio.
Useful links:
Mobile App Penetration Test & Code Review
Cos’è la Cyber Security? Definizione e proposte

Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
ransomware gangs have been targeting businesses in recent times, demanding larger payments than they can extort from consumers. The plan was very successful. According to the new data, 70% of the attacked companies paid the ransom to get their data back. Avoiding ransomware is a necessity, these figures implicitly prove it. If such a large number of companies pay, it is because the risk is too great in terms of reputation and collateral economic losses.
Researchers from IBM Security’s X-Force interviewed executives of 600 companies of all sizes and found that organizations affected by ransomware choose to pay in most cases.
Data shows that 20% of compromised organizations paid ransoms of more than $ 40,000 and 25% paid between $ 20,000 and $ 40,000. These numbers are much higher than that. that consumers typically pay, which is usually around $ 500-1,000, depending on the variant of the ransomware.
When targeting businesses, hacking groups aim to paralyze organizations by encrypting financial data , customer databases, sales data and other vital information .
Avoid ransomware – the risks of attacks
In the past year, a number of organizations have been hit by severe ransomware attacks, including hospitals, universities and others. For example, the San Francisco Municipal Transportation Authority was hit by a ransomware attack during the weekend of Thanksgiving, a very important holiday in the US. The attack paralyzed desktops within the agency and forcing officials to shut down the automatic ticket machines. Needless to say, this attack resulted in a huge loss of assets and a ransom demand.
Getting malware into public organizations isn’t as difficult as you might think, and is often done with a single email .
In their attacks on networks, cybercriminals seek out the servers that keep the business running and encrypt critical assets rather than working on enterprise-wide endpoints.
The access point is usually a phishing email with a malicious attachment, sent to the mailbox of a employee . In most cases, the attachment is a Microsoft Office document asking the victim to enable macros . Clicking the macro enable button is often a trivial matter for those uninformed users who just want to get rid of the warning at the top of the document . The malware runs as soon as the user allows the macros to run. The ransomware can also arrive through any other attachment or through exploit kits which facilitate infection without any special action on your part.
Economic losses
The amount of money businesses have paid to get their data back shouldn’t come as a surprise considering the alternative. As is increasingly the case, the attack doesn’t just put key the data until payment of the requested amount. The threat continues with the release of data if you do not agree to pay a second ransom. In the end two ransoms will be paid and in any case there is no certainty that the data will not be disclosed. (It is said double extortion attack).
Many organizations keep these attacks under wraps to avoid public humiliation and loss of customer confidence . Data from the IBM survey shows that 29% of executives in large corporations would pay more than $ 50,000 to retrieve financial data.
Law enforcement, including the FBI, and security experts advise ransomware victims not to pay, for a variety of reasons. First, there is no guarantee for the attacker to deliver the decryption key. Second, the ransomware’s profits help fund other cybercrime operations.
How to defend yourself to avoid ransomware
Phishing remains one of the key methods by which a ransomware attack is attempted. With the recent increase in remote working, it is imperative to reiterate the importance of being careful when opening emails and attachments . If employees are suspicious of something, they should report it.
Organizations should also make sure they have a good patching strategy and apply the latest security updates . This prevents cybercriminals from taking advantage of known vulnerabilities to distribute malware.
Regularly updating backups should be a priority , because if the worst happens and your organization falls victim to a ransomware attack, your network can be restored without paying the ransom.
SOD provides solutions for the situations listed through the SOCaaS service. You can ensure the protection of a Security Operation Center without having to invest in its initial funding .
The system controls the actions of the computers connected to the network using an artificial intelligence. As soon as a suspicious, even legitimate, action is detected, the technicians are alerted who can investigate the nature of the fact . The new generation SIEM systems and behavioral analysis via UEBA , work together to offer 360 ° security.
SOD also provides intelligent anti-ransomware backup systems via Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud . With this tool at your side, business and customer data are safe. Any attack attempt is identified and mitigated immediately, meanwhile, thanks to dynamic backups, the data is immediately restored .
Avoiding ransomware can be relatively easy – just pay attention to every operation you perform on your computers. Unfortunately, sometimes this is not enough. This is the time when having invested in a quality safety system will make a difference.
For questions or requests do not hesitate to contact us, we will be happy to answer your questions and propose a solution tailored to your needs.


Customers
Twitter FEED
Recent activity
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes L'impatto crescente delle minacce informatiche, su sistemi operativi privati op… https://t.co/FimxTS4o9G
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The growing impact of cyber threats, on private or corporate operating systems… https://t.co/y6G6RYA9n1
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Tempo di lettura stimato: 6 minuti Today we are talking about the CTI update of our services. Data security is… https://t.co/YAZkn7iFqa
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes Il tema della sicurezza delle informazioni è di grande attualità in questo peri… https://t.co/tfve5Kzr09
-
SecureOnlineDesktop
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes The issue of information security is very topical in this historical period ch… https://t.co/TP8gvdRcrF
Newsletter
{subscription_form_1}© 2024 Cyberfero s.r.l. All Rights Reserved. Sede Legale: via Statuto 3 - 42121 Reggio Emilia (RE) – PEC [email protected] Cod. fiscale e P.IVA 03058120357 – R.E.A. 356650 Informativa Privacy - Certificazioni ISO













